What is Cannabis Flower?
What is Cannabis Flower?
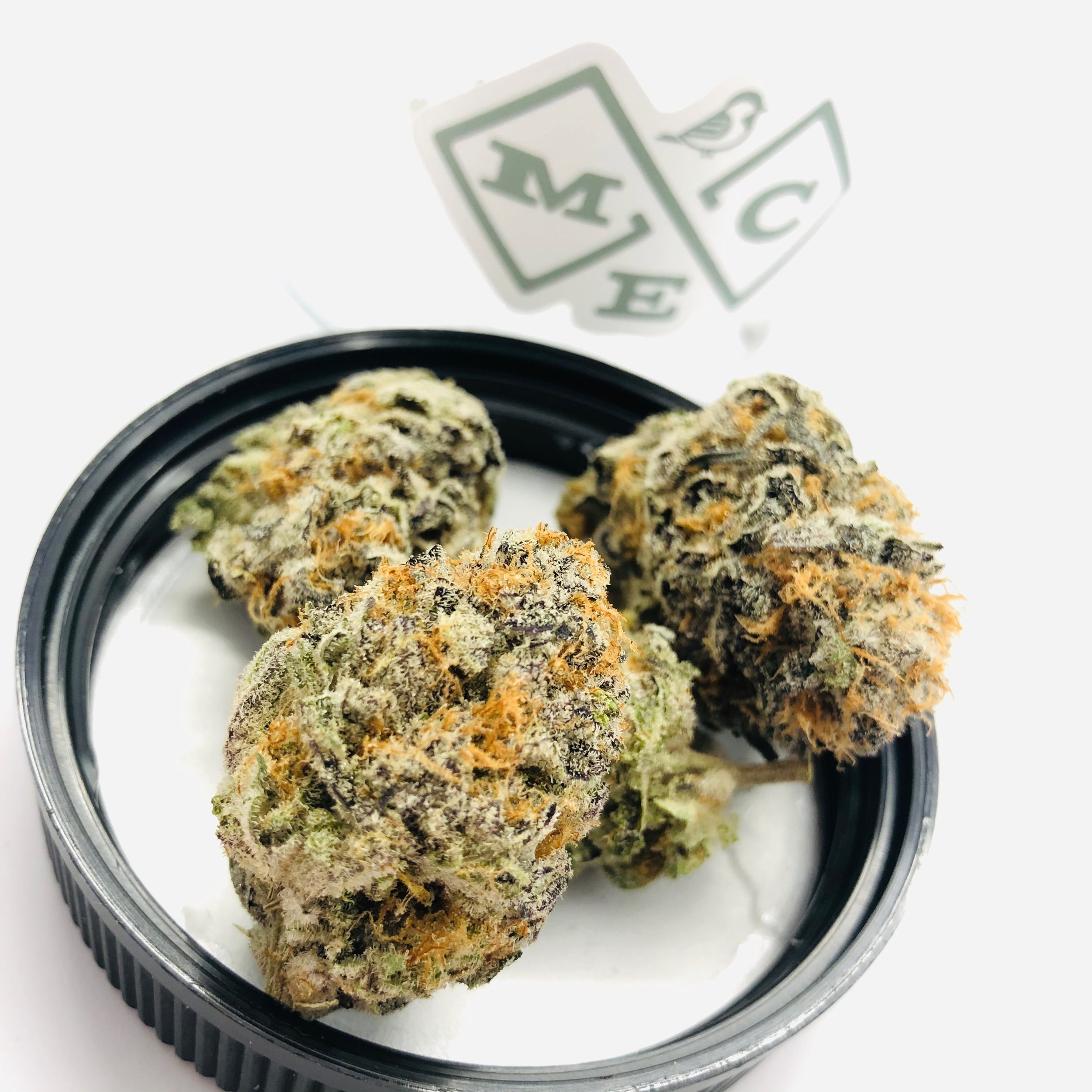
Cannabis is a versatile, therapeutic, and utilitarian plant that has been domesticated by humans dating back to 12,000 years ago. When smoking cannabis, and consuming edibles, topicals, tinctures, and other cannabis preparations, generally it is the female cannabis plant’s cannabinoid-rich flowers that are used. The cannabis plant is identified with more than 550 chemical compounds and over 100 phytochemicals. Cannabis flower contains a full spectrum of these constituents that vary from varietal and cultivar.
Cannabis is dioecious, meaning it is a sexed plant. Male plants produce pollen and are also used for cannabis breeding and textile purposes, while female plants produce flowers used for cannabis therapeutics.
High CBD female hemp plants produce a cannabinoid-rich flower. By definition any cannabis plant in the USA with under 0.3% THC can be considered hemp. So, if you are consuming a product rich in THC, CBD, CBN, CBG, or other cannabinoids, it was derived from cannabis flower. The rest of the plant such as leaves and roots produce only trace amounts of cannabinoids, but can have medicinal value and are often made into teas, tinctures and salves.
Inhaling cannabis flower is a highly popular method of consumption. The rapid entrance into the bloodstream makes it a desirable option for fast acting effects. After the plant is harvested, dried, and cured, all that’s needed to use the flower is to heat it using a dried herb vaporizer or using fire to combust with a pipe, bong or preroll. The heating process separates carboxylic acid from the THC molecule, allowing it to bind with the body’s receptors. That said, unheated cannabis flower has valuable properties too; it can be antispasmodic, anti inflammatory and can regulate the immune system.
Purchasing cannabis flower or “buds” offers you lots of options. You can choose from an array of strains and the paraphernalia you will use to consume it. Many choose to use a grinder to break flower down into smaller pieces inorder increase its surface area, allowing for a more complete burn. There is some belief that grinders can degrade volatile phytochemicals like terpenes or cannabinoid-rich trichomes. Instead, some recommend using a clean sharp pair of scissors. In either case, once ground down you can smoke the material in a bowl, bong, papers, or vaporizer. If not vaporizing, we recommend trying a Mooselabs filter that removes some of the harsh resin and tar. We recommend a dried herb vaporizer for long-term consumption, as it is the cleanest method of inhalation and an excellent investment in your lungs. That said, inhaling any smoke, vapor, or particles contains an inherent risk of lung damage. Please consult your doctor to understand the risks associated with your personal consumption patterns or plans.
High-quality cannabis flower can be produced indoors, outdoors, or in greenhouses. Indoor growing gives the advantage of climate control while presenting the ongoing challenge of providing all variables that a unique cannabis cultivar requires to thrive. The complete control indoor cultivation provides is often prized for the ability to continuously reach the genetic potential of the plant that is reflected in potency and jar appeal. Sungrown or greenhouse grown cannabis often exhibits higher resin and terpene production which can be observed in the stickiness and fragrance of the buds.
Anatomy of cannabis flower
Trichomes
On close inspection, one will notice cannabis flower is covered in trichomes, which are small resin glands that coat the flowers and small leaves near the flowers. These are epidermal hairs that act as a defense to protect the plant during the growing cycle from pests, fungus, and other threats. These small, sparkly glands produce the high concentration of desirable cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids found in cannabis flower. These minuscule mushroom-shaped resin glands, when dried and separated from the plant, are referred to as “kief”. Kief can be consumed in numerous ways such as rolled into hash, consumed in edibles, smoked or processed into extracts.
Cola
A cluster of buds growing together that form large chunks of flower is referred to as colas. The largest colas grow at the top of the plant but you’ll find smaller colas throughout the lower branches
Bract and calyx
The bract is tear shaped and green, encapsulating the reproductive parts of the flower.
The bract is essential to protecting the reproductive parts of the plant through its rigid structure. The calyx, which sticks out of the bract,forms first through small leaves on the base of the flower called sepals. This is a highly resinous part of the anatomy that is home to many of the cannabinoid-rich trichomes and pistils. The bract is essential to the structural function as well as safeguarding the reproductive system of the plant. The bract and calyx are considered the most cannabinoid-dense part of the plant.
Pistil and Stigmas
Pistils are the reproductive organs of flower where the seed will form. stigma grows out of the pistil and serves the purpose of trapping pollen from male plants with their sticky tip. Early in the maturation of the flower, the stigmas are white and will develop into orange, yellow, red, or brown color. Stigmas are partially visible where pistils are covered and protected by the bract.
Sugar leaves
These are the small, trichome-covered leaves that grow out of the flower itself, unlike the large fan leaves that extend from the branches of the plant. Some growers choose to keep these intact when hand trimming as an aesthetic choice and to protect the trichome-dense flower. Other growers choose to manicure them down to not be included in the weight. Since sugar leaves are covered in cannabinoid rich trichomes, leaving them or trimming them is more a matter of aesthetics than of efficacy.
Methods of Consumption
Vaporizer
Vaporizing your flower is a great long term option for people who like the quick effects of inhalation but want to avoid the harshness of combustion. There are many options on the market ranging from small handheld vaporizers to large tabletop devices. Both conduction and convection technology to heat and decarboxylate your flower are available.
Conduction is often found to heat your flower less evenly since the flower is put in direct contact with the heating element. The vapor and smoke production is known to be thicker and larger with these devices. Conduction vapes often requires more cleaning due to the direct contact with the heating element.
Convection has a more even distribution through heating with airflow. Convection has considerably less dense smoke clouds and a smooth and high-quality vapor. Convection-powered devices tend to be at a higher price. Vaporizers offer improved flavor and smell while being less inflammatory than smoking.
Bowls, Bongs, Papers
There can be an overwhelming number of choices when purchasing apparatuses to smoke flower. From artisanal hand-blown glass to convenient to clean and transport silicone, ceramic, stone, and metal pieces, there's an option for every cannabis user based on preference and needs. Glass that utilizes water or ice for a cooling effect can help reduce the burn and coughing caused by smoking flower.
When choosing your paraphernalia consider your preferred amount to consume to conserve the product and achieve the desired dose. When using a bong it can be difficult to control the amount inhaled, whereas using a one-hitter with a small bowl could be an easier way to achieve desired results for a lower-tolerance individual. Hand pipes will have a bowl to pack flower, a carb to place your thumb on to build and release smoke, and a mouthpiece to inhale through. It’s recommended when smoking joints to select papers that are unbleached, organic, and free from added chemicals.
Inhaled cannabis absorption
The effect of inhaled cannabis depends on an array of variables such as cannabinoid percentage in the flower, amount inhaled, side stream of smoke, and absorption. The bioavailability of inhaled cannabis flower is on average 30% THC, ranging between 2%-56%. The volume of smoke inhaled, duration and quantity are all factors that influence absorption. Vaping and smoking tend to have similar levels of bioavailability.
The rapid onset of inhalation allows the user to observe their dose quickly which can be a helpful tool when deciding to inhale more or stop where you currently are. THC is detectable in the systems seconds after inhaling cannabis with the peak concentration of Δ9-THC often between 3-10 minutes after inhaling. The level of THC detected in the body rapidly decreases by 3-4 hours to a low amount.
Unlike edibles, this faster entrance of effects in and out of the body can be highly desirable for a controlled cannabis experience. For those looking to limit the intensity of the psychoactive effects of inhaling THC, a 1:1 CBD:THC flower, or even higher ratio CBD:THC is available on the market. The lower concentration of THC and additional CBD can reduce the psychoactivity of the THC. Personalizing your desired effect and experience is possible with the diversity of choices.
Cannabinoids in cannabis flower
Humans and cannabis have evolved a lock and key relationship via our endocannabinoid system (ECS). THE ECS is a complex cell-signaling system that modulates the nervous and immune systems and other organ systems through a system of receptors and chemical signaling. Your endocannabinoid system is present and activated even when not using cannabis and cannabinoids. This system has an intricate role in the regulation of mood, appetite, pain sensation, vascular and nonvascular smooth muscle tone, and immune function.
Cannabinoids found in cannabis flower interact with our endocannabinoid system in so many ways including through our CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Raw cannabinoids like THCA, CBDA, CBNA, and CBGA are converted to THC, CBD, CBN, and CBG when decarboxylated with heat. These decarboxylated molecules can bind or become available to your cannabinoid receptors. This, for example, is why THC is psychoactive whereas THCA is not. If you don’t heat your flower it will not create a high. This decarb process is the defining difference in effect between eating a raw bud that will not interact with your system like THC and eating an edible that has undergone the heating process to convert THCA to THC. The raw acidic molecules naturally occurring in the plant are found beneficial but will interact with your ECS differently.
Flower is an excellent way for individuals to seek fast-acting relief as well as experiment with dose, strain, and paraphernalia of choice. With the quickest onset of cannabis administration and differing concentrations of cannabinoids, one has the ability to customize their experience by consuming cannabis flower.
1.https://phys.org/news/2021-07-cannabis-domesticated-years.html#:~:text=Cannabis%20has%20been%20used%20for,plants%20from%20across%20the%20world.Phys Org. Cannabis first domesticated 12,000 years ago: study. Isle of Man. 2021.
2. https://thcdesign.com/blog/cannabis-plant-anatomy/ THC Design. Breaking Down the Cannabis Plant. California
3.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312152737_The_Cannabis_Plant_Botanical_Aspects Sayed Farag and Oliver Kayser. The Cannabis Plant: Botanical Aspects. 2017. London, United Kingdom
4.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16237477/#:~:text=THC%20bioavailability%20averages%2030%25.,and%20absorption%20is%20highly%20variable. National Library of Medicine. Pharmacokinetics of cannabinoids. 2005. Bethesda, Maryland.
5.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9336020/
National Library of Medicine.Pharmacology of cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors.1997
Bethesda, Maryland.